Quick Links
Wi-Fi technology has been evolving rapidly due to advancements in automotive solutions, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and virtual and augmented reality technologies. The latest 5G technology has propelled the Wi-Fi alliance to develop new wireless standards that can efficiently handle the vast amounts of data being consumed and processed by consumers and businesses. The latest Wi-Fi 7 brings several improvements over its predecessor, Wi-Fi 6E.
What is Wi-Fi 7?
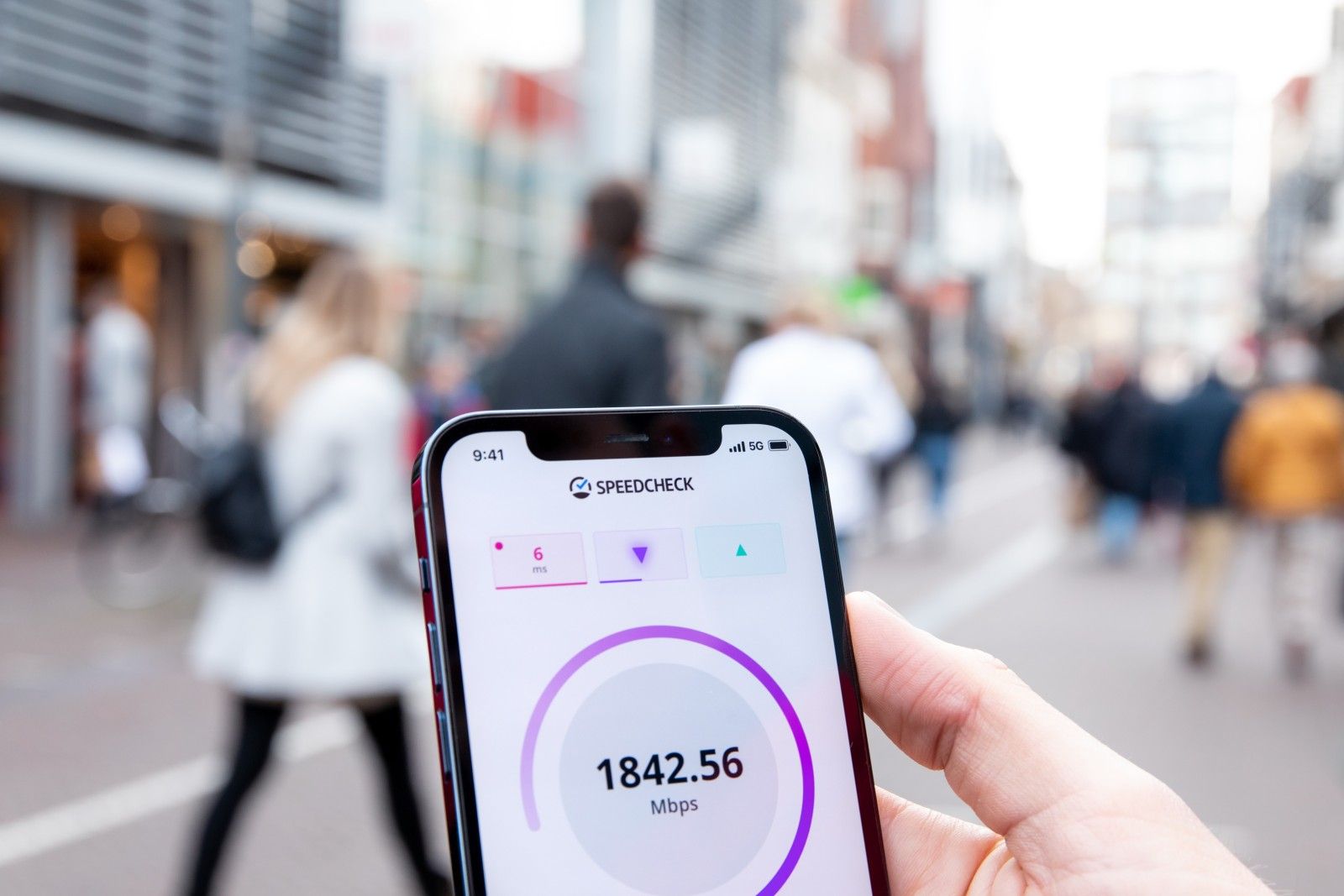
Wi-Fi 7 is the most recent standard, officially launched on January 8, 2024, by the Wi-Fi Alliance. This standard offers several new features and benefits, including up to 2x higher throughput, deterministic latency, increased efficiency, and greater reliability. Wi-Fi 7 improves transmission rates by 20% and reduces transmission overhead.
- 320 MHz channels: available in countries that make the 6 GHz band available to
- Wi-Fi, ultra-wide channels double today’s widest channel size to facilitate multigigabit device speeds and high throughput
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): allows devices to transmit and receive data simultaneously over multiple links for increased throughput, reduced latency, and improved reliability
- 4K QAM: achieves 20% higher transmission rates than 1024 QAM
- 512 Compressed block-ack: improves efficiency and reduces overhead
- Multiple RUs to a single STA: improves flexibility for spectrum resource scheduling to enhance spectrum efficiency
- Triggered Uplink Access: optimizes Wi-Fi 6 defined triggered uplink access to accommodate latency-sensitive streams and satisfy QoS requirements
- Emergency Preparedness Communication Services (EPCS): provides a seamless National Security & Emergency Preparedness (NSEP) service experience to users while maintaining the priority and quality of service in Wi-Fi access networks
The next-generation Wi-Fi is already available from several companies, and TP-Link, Netgear, and Eero are among the first to release new routers with Wi-Fi 7. Qualcomm and MediaTek have also announced new chips with the new connectivity tool.
Wi-Fi 7 vs Wi-Fi 6E: Benefits and Key Features
- Faster Speeds: Wi-Fi 7 can reach speeds up to 46Gbps, significantly faster than Wi-Fi 6E’s approximately 9Gbps. Wi-Fi 7 devices and compatible routers can effectively replace Ethernet and wired connections where wireless solutions were previously unsuitable, eliminating the need for cables.
- Less Interference: The new standard will use several recent advancements and solutions to prevent interference with other devices. Wi-Fi 7 will utilize the 6GHz band, similar to Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 6. However, there are several enhancements ensuring the new standard works better and remains more reliable than previous versions. For instance, Wi-Fi 7 will use the 320 MHz channel, which is much wider than the channels used by previous generations. When the band and the wider channels are combined, it’ll result in less interference, ultimately providing a better and more reliable experience.
- Low Latency: Wi-Fi 7 can transmit and receive data simultaneously over many links and in various frequencies, enabling faster file transfers. Thanks to the improvements in this new solution, the latency has been significantly reduced.
All of these enhancements make Wi-Fi 7 more stable, reliable, and significantly faster. It allows users to transfer data more quickly and with lower latencies, enabling developers to create a more immersive AR/VR experience with more realistic 3D content. Future cars will be able to transfer files and communicate faster, and streaming could also gain major enhancements that reduce latency and improve the performance of games and software.
How is Wi-Fi 7 going to change the way you interact with your devices
Wi-Fi 7 not only unlocks faster transfer speeds but also offers a more reliable connection, less interference from other devices and IoT devices, and lower latency. If you plan on upgrading your router, you’ll instantly get these improvements, although you’ll need a Wi-Fi 7-enabled device to take advantage of the new enhancements. Luckily for those using devices that support Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E, they’ll still be able to use the new router. The Wi-Fi 7 standard is backward compatible; however, you might not benefit from the new improvements unless you upgrade your network card, laptop, tablet, and other devices.
Once you get the power of Wi-Fi 7 in your hands, in the form of a compatible device, you’ll see less interference, improved loading speeds, and lower latency. While these might not be noticeable from day-to-day internet surfing, the improvements will significantly enhance the streaming and gaming experience, and compatible IoT devices should benefit from faster speeds and fewer connection drops.
The new multi-link operation will also enable Wi-Fi 7 to tap into both 6GHz and 5GHz bands at the same time to prevent bottlenecks and keep you connected once the user is out of range. The multi-link operation will also enable devices to simultaneously send and receive data across the two bands, increasing throughput and making the entire connection more stable.
Furthermore, new cars, and AR/VR/MR headsets will be able to wirelessly communicate and stream, improving real-time responsiveness and providing a more immersive experience. The ability to transfer larger files without interruptions and bottlenecks should enable developers to create even more realistic environments and help advance the progress of various AI tools in the future.